Understanding Taxable Income and Tax Calculation in UAE Corporate Tax: A Guide for Businesses
- May 28, 2023
- Posted by: GITPAC
- Categories: Startups, TAX, UAE, UAE Corporate Tax, UAE FEDERAL TAX AUTHORITY

In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), corporate tax regulations play a crucial role in shaping the business landscape. It is essential for businesses operating in the UAE to have a comprehensive understanding of taxable and exempt persons, as well as the calculation of taxable income. This article provides an overview of these key concepts and their implications for corporate tax obligations.
Exempt Persons in UAE Corporate Tax:
Certain entities and activities are exempt from corporate tax in the UAE. This section delves into the criteria that grant exemption to specific categories, such as non-profit organizations, government entities, and companies engaged in specific sectors. Exploring these exemptions allows businesses to evaluate their eligibility and take advantage of potential tax benefits.
 In addition to not being subject to Corporate Tax, Government Entities, Government Controlled Entities that are specified in a Cabinet Decision, Extractive Businesses and Non-Extractive Natural Resource Businesses may also be exempted from any registration, filing and other compliance obligations imposed by the Corporate Tax Law, unless they engage in an activity which is within the charge of Corporate Tax.
In addition to not being subject to Corporate Tax, Government Entities, Government Controlled Entities that are specified in a Cabinet Decision, Extractive Businesses and Non-Extractive Natural Resource Businesses may also be exempted from any registration, filing and other compliance obligations imposed by the Corporate Tax Law, unless they engage in an activity which is within the charge of Corporate Tax.
Taxable Persons
Taxable persons, on the other hand, are individuals or entities that are subject to corporate tax on their taxable income. The FTA sets out criteria to identify taxable persons in the UAE. Some key points to consider include:
- Companies incorporated in the UAE, including free zone companies and limited liability companies.
- Branches of foreign companies operating in the UAE.
- Partnerships and joint ventures.
- Permanent establishments of foreign companies.
- Non-profit organizations engaged in commercial activities.
Taxable persons are required to calculate and pay corporate tax based on their taxable income, as determined by the guidelines provided by the FTA.
Residence for Corporate Tax purposes is not determined by where a person resides or is domiciled but instead by specific factors that are set out in the Corporate Tax Law. If a Person does not satisfy the conditions for being either a Resident or a Non-Resident person then they will not be a Taxable Person and will not therefore be subject to Corporate Tax.
Taxable Income Calculation
The process of calculating taxable income is crucial for taxable persons to fulfill their tax obligations accurately. The FTA provides guidelines on determining taxable income, which includes the following elements:
What is Taxable Income?
Taxable income refers to the portion of a company’s revenue that is subject to corporate tax. In the UAE, taxable income is determined based on the guidelines provided by the Federal Tax Authority (FTA). It includes various components such as:
- Gross Income: Gross income comprises all revenue generated from business activities, including sales, services, and other sources of income.
- Deductible Expenses: Allowable expenses directly related to business operations, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and other costs, can be deducted from gross income.
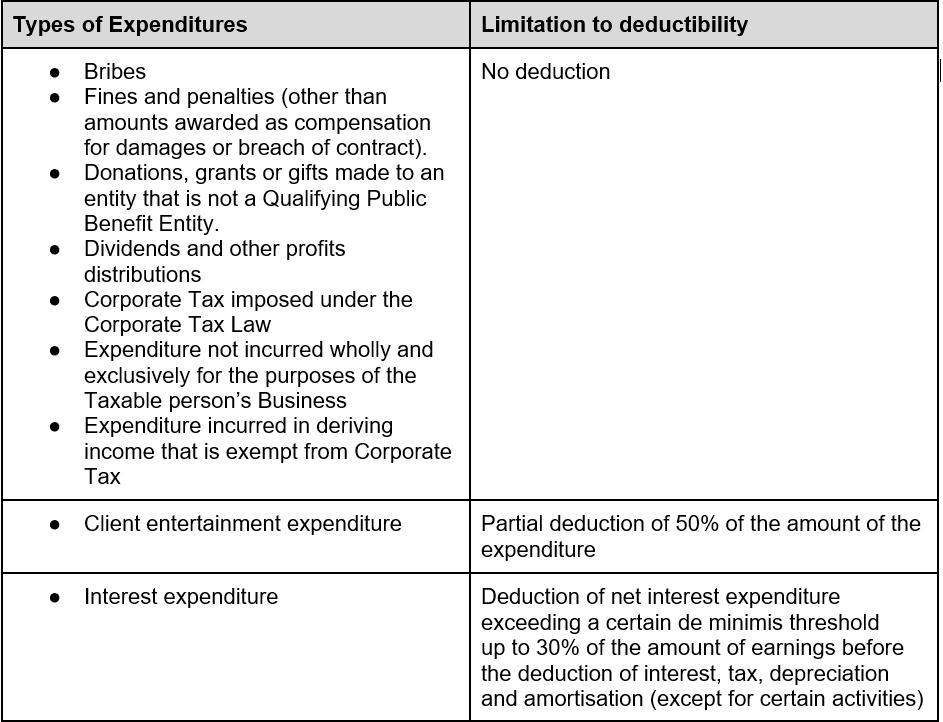
- Non-Deductible Expenses: Certain expenses, such as fines and penalties, personal expenses, and non-business-related costs, are not deductible for tax purposes.
- Tax Exemptions and Allowances: The FTA provides specific exemptions and allowances for certain sectors and activities, which can reduce the taxable income.
Tax Rates
The corporate tax rate in the UAE is 9%. However, there is a lower tax rate of 0% for taxable income that is below AED 375,000.
Tax Filing
Taxable persons are required to file a corporate tax return with the Federal Tax Authority (FTA) by the end of the month following the end of their financial year.
Penalties
Failure to file a corporate tax return or to pay the correct amount of tax can result in penalties being imposed by the FTA. These penalties can be significant, so it is important to ensure that all corporate tax obligations are met.
Tax Calculation Methods
The UAE corporate tax system employs a progressive tax rate structure based on the company’s taxable income. The tax rates are applied in a tiered manner, with higher tax rates for higher income brackets. The specific tax rates are determined by the FTA and are subject to change.
To calculate the corporate tax liability, businesses follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the Gross Income – Calculate the total revenue generated from business operations, including sales, services, and other sources of income.
Step 2: Deduct Allowable Expenses – Subtract the allowable expenses, such as salaries, rent, utilities, and other costs, from the gross income.
Step 3: Apply Exemptions and Allowances – Deduct any tax exemptions and allowances provided by the FTA for specific sectors or activities.
Step 4: Arrive at the Taxable Income – Subtract the deductions (allowable expenses and exemptions) from the gross income to obtain the taxable income.
Step 5: Apply the Tax Rate – Determine the applicable tax rate based on the taxable income bracket and calculate the corporate tax liability accordingly.
Example
Let’s say that you are a resident of the UAE and your taxable income for the year is AED 1,000,000. You have allowable deductions of AED 200,000. Your taxable income would be calculated as follows:
Taxable Income = Total Income - Allowable Deductions
= AED 1,000,000 - AED 200,000
= AED 800,000
Taxable Income and Tax Calculation for Non-Residents
Non-residents are only taxed on income that is sourced in the UAE. This means that if you are a non-resident of the UAE and you earn income from a source outside of the UAE, you will not be taxed on that income.
To calculate taxable income for non-residents, you will need to add up all of your income from sources inside the UAE. Then, you will need to subtract any allowable deductions. Allowable deductions for non-residents are the same as for residents.
Example
Let’s say that you are a non-resident of the UAE and your taxable income for the year is AED 500,000. You have allowable deductions of AED 100,000. Your taxable income would be calculated as follows:
Taxable Income = Total Income - Allowable Deductions
= AED 500,000 - AED 100,000
= AED 400,000
Tax Rate
The corporate tax rate for non-residents is 9%. In this example, your taxable income is above AED 375,000, so you will pay the standard corporate tax rate of 9%.
Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with UAE corporate tax regulations is vital to avoid penalties and maintain a good standing with the tax authorities. Businesses are required to maintain accurate financial records, including income statements, expense records, and documentation of tax exemptions and allowances claimed.
Annual tax returns must be filed with the FTA, providing details of the taxable income, deductions, and tax liability calculations. It is crucial to meet the filing deadlines and ensure that the tax returns are accurately prepared to reflect the company’s financial position
Understanding the distinction between exempt and taxable persons is crucial for businesses and individuals operating in the UAE. By adhering to the guidelines provided by the FTA, organizations can ensure compliance with corporate tax regulations. Proper calculation of taxable income and awareness of exemptions and allowances can help businesses manage their tax liabilities effectively. Stay informed and consult with tax professionals to navigate the intricacies of UAE corporate taxation.
